
Kyphoplasty Procedure: What Patients Can Expect
What is Kyphoplasty?
Kyphoplasty Procedure: A surgical treatment for painful vertebral compression fractures, where a small balloon is inserted into the fractured vertebra, creating space. This space is then filled with special bone cement, providing immediate pain relief and stabilizing the spine. Kyphoplasty significantly improves patients’ quality of life by restoring vertebral height and reducing spinal deformity. It’s a safe and effective treatment with minimal recovery time.
Kyphoplasty Procedure: A Step-by-Step Guide
- Preparation for Kyphoplasty
- Patients undergo imaging tests like X-rays, CT scans, or MRIs.
- A physical exam is performed to assess the patient’s condition.
- Medications may be adjusted, especially blood thinners or NSAIDs.
- The Day of the Procedure
- Patients are advised to fast for at least 6 hours before the procedure.
- Local anesthesia and light sedation are administered.
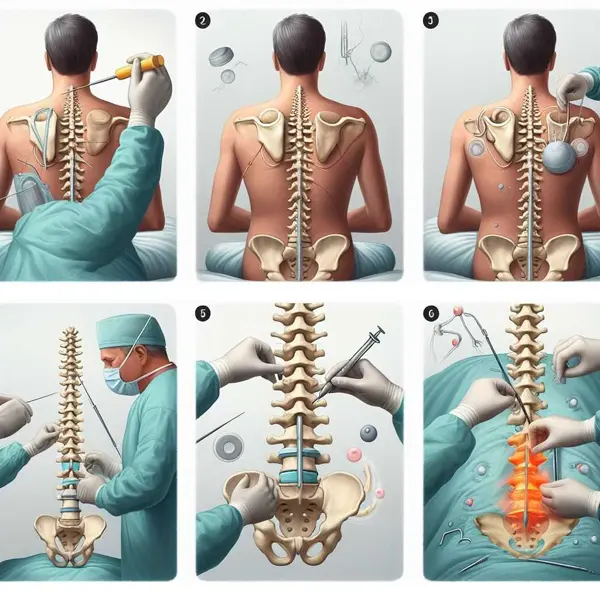
- Performing Kyphoplasty
- A small incision is made in the back.
- A narrow tube is inserted through the incision under fluoroscopy (x-ray guidance).
- A special balloon (bone tamp) is guided into the vertebra and inflated to create space.
- The balloon is removed, and the cavity is filled with a cement-like material called polymethylmethacrylate (PMMA).
- The PMMA hardens quickly, stabilizing the bone.
- Post-Procedure Care
- Patients are observed in a recovery room for a couple of hours.
- Pain relief is often immediate, and patients can return to regular activities shortly.
- Benefits of Kyphoplasty
- It helps restore vertebral height and correct spinal deformity.
- Provides stabilization and pain relief.
- Involves a short recovery period with a low risk of complications.
This procedure is particularly beneficial for patients with osteoporosis-related fractures or those with certain types of spinal tumors. It’s designed to offer quick pain relief and help patients return to their normal activities as soon as possible.
How Kyphoplasty Repairs Spinal Fractures
- Stabilizing the Vertebrae
- Kyphoplasty uses a balloon-like device to create space within the collapsed vertebra.
- The procedure prevents further collapse and restores the spine’s natural shape.
- Injecting Bone Cement
- After creating space, a special cement (polymethylmethacrylate or PMMA) is injected.
- This cement hardens quickly, providing immediate stability to the fractured vertebra.
- Relieving Pain
- By stabilizing the fracture, kyphoplasty can significantly reduce back pain.
- It prevents microscopic movements at the fracture site that can cause pain.
- Improving Spinal Deformity
- Kyphoplasty can correct kyphosis, a condition where the spine curves and causes a hunchback appearance.
- It helps maintain the spine’s proper alignment and prevents further deformity.
- Enhancing Mobility
- Patients often experience improved mobility after the procedure.
- It allows individuals to return to their daily activities with less discomfort.
- Preventing Future Fractures
- By restoring strength to the weakened vertebra, kyphoplasty can help prevent future fractures in the same area.
Kyphoplasty is a valuable treatment option for patients with painful spinal fractures, offering a minimally invasive solution with a quick recovery time and significant improvements in pain and mobility.
The Role of Interventional Radiology in Kyphoplasty Procedure
- Utilizing Imaging for Precision
- Interventional radiologists use fluoroscopy, a type of continuous X-ray, to guide the kyphoplasty procedure.
- This live imaging allows for real-time visualization of the spine and accurate placement of instruments.
- Minimally Invasive Approach
- The procedure is performed through a small incision, minimizing tissue damage, and promoting faster healing.
- Interventional radiology techniques reduce the need for traditional open surgery.
- Expertise in Patient Care
- Interventional radiologists are trained to perform these specialized procedures with the utmost care5.
- They work closely with patients to manage pain and provide post-procedure follow-up.
- Advancing Spinal Health
- Kyphoplasty represents a significant advancement in the treatment of spinal fractures, largely due to interventional radiology.
The field continues to evolve, offering new techniques and technologies to improve patient outcomes.
How Kyphoplasty Works
- Initial Assessment
- Patients undergo diagnostic imaging, such as X-rays, MRI, or CT scans, to locate and assess the fracture.
- These images help determine if kyphoplasty is the appropriate treatment.
- Preparation for Surgery
- Before the procedure, patients may need to fast and adjust their medications, especially if they’re on blood thinners.
- An intravenous line (IV) is placed for anesthesia and other medications.
- The Kyphoplasty Procedure
- The patient lies face down, and the area of the back where the needle will be inserted is sterilized.
- Local anesthesia is applied to numb the area.
- A small incision is made, and a hollow needle (trocar) is inserted through the skin.
- Using fluoroscopy, a type of real-time X-ray, the needle is guided to the correct position in the vertebra.
- A balloon device is inserted through the needle into the vertebra and inflated. This creates space and restores some of the lost vertebral height.
- The balloon is deflated and removed, leaving a cavity that is filled with a special bone cement, polymethylmethacrylate (PMMA).
- The cement hardens quickly, stabilizing the bone and providing immediate pain relief.
- Post-Procedure Care
- After kyphoplasty, patients are monitored for a short period before being discharged.
- Pain relief is often immediate, and patients can usually return to normal activities within a day or two.
- Benefits of Kyphoplasty
- The procedure is minimally invasive, with a low risk of complications.
- It provides rapid pain relief and can help restore spinal alignment and height.
Benefits of Kyphoplasty Procedure
- Pain Relief
- Kyphoplasty can significantly reduce or eliminate pain caused by compression fractures.
- The stabilization of the spine after the procedure often results in immediate pain relief.
- Prevention of Deformity
- The procedure helps prevent kyphosis, which is a hunched-over posture that can occur due to spinal fractures.
- By restoring the height of the vertebrae, kyphoplasty can help maintain a more natural spine alignment.
- Minimally Invasive
- Kyphoplasty is a minimally invasive procedure, typically involving only a small puncture rather than a large incision.
- This leads to a shorter procedure time and less trauma to the body compared to traditional surgery.
- No Extensive Rehabilitation
- Unlike many surgical procedures, kyphoplasty usually does not require physical therapy or extensive rehabilitation post-surgery.
- Patients can often quickly return to their regular activities.
- Improved Quality of Life
- With the reduction in pain and the ability to return to daily activities, patients often experience an improved quality of life.
- The procedure can also lead to improved mobility, allowing patients to move more freely without discomfort.
- Restored Height and Reduced Hunching
- Kyphoplasty can help restore the height of compressed vertebrae, which may have been lost due to the fracture.
- This contributes to a straighter posture and reduced hunching, helping patients stand up straighter.
- Reshaped Vertebrae
- The procedure allows for the reshaping of the vertebrae, which can be beneficial for long-term spinal health.
- Fast Recovery
- Most patients experience a fast recovery time, with many returning home the same day as the procedure.
These benefits make kyphoplasty a compelling option for patients with vertebral compression fractures, offering a combination of immediate pain relief and long-term improvements in spinal health and function.
Who Can Benefit from Kyphoplasty?
- Patients with Osteoporosis-Related Fractures
- Individuals with osteoporosis are prone to developing compression fractures due to weakened bones.
- Kyphoplasty can help stabilize the spine and alleviate pain caused by these fractures.
- Elderly Patients
- As people age, the risk of spinal fractures increases.
- Elderly patients, who may not be suitable for more invasive surgeries, can often undergo kyphoplasty safely.
- Cancer Patients
- Cancer that has metastasized to the spine can lead to fractures.
- Kyphoplasty can provide pain relief and improve the quality of life for these patients.
- Individuals with Physical Jobs
- Those with physically demanding jobs are at risk for vertebral fractures due to heavy lifting and repetitive motions.
- Kyphoplasty can help such individuals return to work and manage the pain from fractures.
- Patients with Chronic Back Pain
- If chronic back pain is due to vertebral fractures and other therapies have failed, kyphoplasty might be an effective treatment.
- Patients with Recent Fractures
- Kyphoplasty is most effective when performed on recent fractures.
- It’s important to seek medical advice promptly if a spinal fracture is suspected.
Kyphoplasty offers a minimally invasive option for pain relief and spinal stabilization for patients suffering from vertebral compression fractures due to various conditions.
Safety and Recovery in Kyphoplasty
- Safety Aspects
- Kyphoplasty is considered a low-risk procedure with a high success rate.
- Complications are rare, but patients are monitored for signs such as infection, bleeding, or cement leakage.
- Interventional radiologists use real-time imaging to minimize risks during the procedure.
- Immediate Post-Procedure Care
- Patients may experience some soreness at the needle insertion site, but this typically resolves within a few days.
- Most individuals can start walking an hour after the procedure and go home the same day.
- Recovery Timeline
- Pain relief is often rapid, and complete recovery is expected within four to six weeks.
- Patients are usually able to return to work and normal activities significantly sooner.
- Heavy lifting and strenuous activities should be avoided for at least four to six weeks.
- Follow-Up Care
- Follow-up appointments are important to ensure that the vertebrae are healing properly.
- Imaging tests, such as X-rays, may be scheduled within the first week after surgery to evaluate the effectiveness of the bone cement.
- Long-Term Recovery
- Communication with healthcare providers is critical for a smooth recovery process.
- Patients are advised to report any issues such as increased pain, fever, or unusual symptoms immediately.
- Lifestyle Adjustments
- After kyphoplasty, patients may need to make temporary lifestyle adjustments to aid recovery.
- Activities that involve bending, twisting, or lifting should be limited during the initial recovery phase.
- Bone Health Management
- Patients are encouraged to discuss bone-strengthening supplements and lifestyle changes with their doctor to prevent future fractures.
The safety and recovery process of kyphoplasty emphasizes minimal discomfort and a quick return to daily life, making it a favorable option for many patients suffering from vertebral compression fractures.
Kyphoplasty in the Future of Medicine: Advancements and Prospects
- Technological Innovations
- Future advancements in imaging technology will likely enhance the precision of kyphoplasty procedures.
- Robotics and computer-assisted navigation may be integrated to improve outcomes and reduce risks.
- Material Science Developments
- Research into new biocompatible materials could lead to alternatives to PMMA cement, offering better integration with the body’s natural tissues.
- The development of bioactive cements that promote bone growth and healing is a potential area of innovation.
- Customized Patient Care
- Personalized medicine approaches may tailor kyphoplasty procedures to individual patient’s anatomy and health needs.
- Genetic research could influence how kyphoplasty is used in conjunction with other treatments for bone health.
- Expanding Indications
- Kyphoplasty might be applied to a broader range of spinal conditions as techniques and materials improve.
- It could also become a preventive measure for patients at high risk of fractures due to osteoporosis or other bone-weakening conditions.
- Training and Education
- Enhanced simulation models for training interventional radiologists will likely improve the safety and efficacy of kyphoplasty.
- Educational programs may expand, emphasizing the importance of early detection and treatment of spinal fractures.
- Global Access and Affordability
- Efforts to make kyphoplasty more accessible and affordable worldwide could increase its utilization in developing countries.
- Insurance coverage and healthcare policies may adapt to support the broader use of kyphoplasty as a cost-effective treatment option.
- Clinical Research and Trials
- Ongoing clinical trials will continue to assess the long-term benefits and potential risks of kyphoplasty.
- Research may also explore the combination of kyphoplasty with other treatments, such as osteoporosis medications, to enhance patient outcomes.
The future of kyphoplasty in medicine is intertwined with advancements in technology, material science, and patient care strategies. As research progresses, kyphoplasty is expected to become an even more integral part of spine health management, offering improved solutions for patients suffering from spinal fractures.
Conclusion
In conclusion, kyphoplasty is a surgical procedure that has proven to be effective in treating spinal fractures. It offers significant pain relief and improved stability for patients suffering from conditions such as osteoporosis, cancer, or traumatic spinal injuries1. The procedure involves the insertion of a balloon into the fractured vertebra, followed by the application of a special cement to stabilize the structure2.
Patients typically experience a relatively quick recovery period, and the procedure allows for a return to regular activities shortly after2. However, it’s important to note that the success of kyphoplasty depends on proper patient selection and a thorough consideration of potential risks1. While the effectiveness of kyphoplasty is generally well-regarded, there is ongoing debate and it’s essential to discuss the risks and benefits with a healthcare provider3.
Overall, kyphoplasty may significantly improve a person’s quality of life and mobility, reducing the need for pain relief medication and preventing further spinal deformity3.
Commonly Asked Questions about "Kyphoplasty Procedure"
- During Kyphoplasty, the surgeon makes a small incision in the back and inserts a narrow tube into the fractured vertebra under fluoroscopic guidance. A balloon is then inserted through the tube and inflated to create a cavity within the vertebral body. Once the cavity is formed, the balloon is deflated and removed, and bone cement is injected into the space to stabilize the fracture.
- Kyphoplasty is primarily used to treat painful vertebral compression fractures caused by osteoporosis, spinal tumors, or trauma. It can help relieve pain, restore vertebral height, and improve spinal alignment in patients with compression fractures.
- Kyphoplasty is considered a minimally invasive procedure and is typically performed on an outpatient basis under local or general anesthesia. It involves small incisions and minimal tissue disruption, resulting in shorter recovery times compared to traditional open surgery.
- While kyphoplasty is generally safe, like any medical procedure, it carries some risks. Potential complications may include infection, bleeding, nerve injury, allergic reaction to anesthesia or bone cement, and leakage of cement into surrounding tissues. However, serious complications are rare.
- Recovery time after kyphoplasty varies from patient to patient but is typically faster than traditional open surgery. Most patients experience pain relief immediately after the procedure and can resume light activities within a few days. Full recovery may take several weeks, during which time patients are advised to avoid strenuous activities and heavy lifting.
- Kyphoplasty has been shown to be highly effective in reducing pain, improving function, and restoring vertebral height in patients with vertebral compression fractures. Studies have reported success rates ranging from 70% to 90%, with the majority of patients experiencing significant pain relief and improved quality of life following the procedure.



