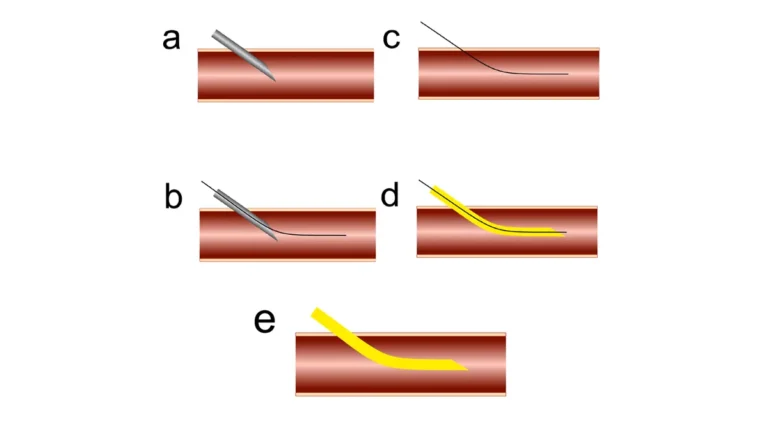
Procedure:
The Seldinger Technique is a fundamental method used in various medical procedures to access blood vessels or hollow organs safely. Here’s a step-by-step guide to the Seldinger technique:
The Step-by-step guide to the Seldinger technique
- Preparation: Gather all necessary equipment, including a needle, guidewire, dilator, and catheter. Ensure that the patient is properly positioned and adequately prepared for the procedure.
- Anesthesia: Administer local anesthesia to the skin and subcutaneous tissues at the entry site to minimize discomfort during the procedure.
- Selection of Entry Site: Choose an appropriate entry site for vessel access, typically a location with easy anatomical landmarks and minimal risk of complications.
- Needle Insertion: Using a sterile technique, insert a hollow needle perpendicularly into the skin at the selected entry site. Advance the needle slowly and steadily until blood is aspirated into the syringe, indicating successful entry into the vessel.
- Guidewire Insertion: Once the needle is properly positioned within the vessel lumen, carefully advance a flexible guidewire through the needle into the vessel. Ensure smooth and controlled movement of the guidewire to prevent damage to the vessel walls.
- Needle Removal: With the guidewire securely in place, remove the needle while maintaining control over the guidewire to prevent its dislodgment or migration.
- Inserting the Dilator: Guide the tapered dilator over the guidewire into the vessel, employing a gentle twisting motion to ease its passage through the tissue layers.
- Dilator Removal: After adequate dilatation of the entry site, remove the dilator while leaving the guidewire in place to maintain access to the vessel.
- Catheter Insertion: Advance the desired catheter or medical device over the guidewire into the vessel or target organ. Ensure proper positioning and secure fixation of the catheter to prevent accidental displacement.
- Guidewire Removal: Once the catheter is securely in place, carefully withdraw the guidewire while maintaining the catheter position to avoid disrupting its placement.
- Confirmation of Placement: Verify the correct placement of the catheter or medical device using appropriate imaging modalities such as fluoroscopy, ultrasound, or contrast injections.
- Securement and Dressing: Secure the catheter in place using a suture or adhesive dressing to prevent accidental dislodgment. Apply sterile dressings to the entry site to minimize the risk of infection.
- Post-procedure Monitoring: Monitor the patient closely for any signs of complications, such as bleeding, hematoma formation, or vascular injury. Provide appropriate post-procedure care and instructions to the patient.
By following these steps carefully and adhering to best practices in sterile technique, healthcare providers can safely and effectively perform procedures using the Seldinger technique to access blood vessels and hollow organs.
Applications Across Medical Specialties:
The versatility of the Seldinger Technique transcends numerous medical specialties, including but not limited to:
- Interventional Radiology: In procedures such as angiography, embolization, and percutaneous biopsies, the Seldinger Technique facilitates precise access to target vessels or organs, enabling therapeutic and diagnostic interventions.
- Critical Care Medicine: Central venous catheterization, a common procedure in critical care settings, relies heavily on the Seldinger Technique for safe and efficient central venous access.
- Cardiology: From coronary angiography to pacemaker implantation, cardiologists harness the Seldinger Technique to navigate complex vascular structures and deliver life-saving therapies with precision.
- Emergency Medicine: Rapid vascular access is paramount in emergency situations. The Seldinger Technique allows emergency physicians to swiftly establish venous or arterial access for resuscitative measures and medication administration.
Advantages and Limitations:
The adoption of the Seldinger Technique offers several advantages over traditional surgical methods, including:
- Minimally Invasive: By obviating the need for open surgery, the Seldinger Technique reduces trauma, postoperative pain, and recovery time for patients.
- Versatility: Its applicability across various medical specialties underscores the versatility and adaptability of the Seldinger Technique to diverse clinical scenarios.
- Reduced Complications: With meticulous technique and appropriate training, the risk of complications such as bleeding, infection, and nerve injury is minimized.
However, it is crucial to acknowledge the limitations and potential risks associated with the Seldinger Technique, including:
- Risk of Vascular Injury: Improper needle placement or guidewire manipulation can lead to vascular injury, hematoma formation, or pseudoaneurysm.
- Infection: Despite adherence to aseptic principles, the risk of local or systemic infection remains inherent to any invasive procedure.
- Skill Dependence: Proficiency in the Seldinger Technique requires extensive training and hands-on experience to mitigate procedural errors and optimize patient outcomes.
Conclusion:
In the ever-evolving landscape of modern medicine, the Seldinger Technique continues to serve as a cornerstone of innovation and progress. Its widespread adoption across diverse medical specialties underscores its enduring significance in enhancing patient care, safety, and procedural efficiency. By mastering the principles and techniques of the Seldinger Technique, healthcare professionals empower themselves to deliver optimal outcomes and usher in a new era of minimally invasive interventions.
- The Seldinger technique is a medical procedure used to gain access to blood vessels or hollow organs. It involves the insertion of a hollow needle into the desired structure, followed by the introduction of a guidewire through the needle, and subsequent placement of medical devices or catheters over the guidewire.
- The Seldinger technique was developed by Dr. Sven-Ivar Seldinger, a Swedish radiologist, in 1953. His innovative approach revolutionized vascular access procedures and became a cornerstone of modern interventional medicine.
- The Seldinger technique offers several advantages, including reduced risk of vascular injury, precise placement of medical devices, and the ability to perform minimally invasive procedures with less trauma to surrounding tissues.
- The Seldinger technique is commonly used in a variety of medical procedures, including central venous catheterization, arterial blood gas sampling, percutaneous transluminal angioplasty, percutaneous nephrostomy, and percutaneous liver biopsy, among others.
- When performed by trained healthcare professionals using appropriate sterile technique and imaging guidance, the Seldinger technique is considered safe and effective for accessing blood vessels and hollow organs. However, like any medical procedure, it carries some risks, including bleeding, infection, and vessel injury.
- The Seldinger technique involves the sequential insertion of a hollow needle into the target structure, followed by the passage of a guidewire through the needle into the vessel or organ. Once the guidewire is in place, medical devices or catheters can be advanced over the guidewire into the desired location.
- To perform the Seldinger technique effectively, healthcare providers should carefully select the entry site, use appropriate imaging guidance to confirm needle placement, advance the guidewire smoothly and cautiously, and confirm correct placement of medical devices using imaging modalities such as fluoroscopy or ultrasound.
- While complications with the Seldinger technique are relatively rare, they can include bleeding, hematoma formation, infection, vascular injury, and inadvertent puncture of adjacent structures. Healthcare providers should be trained to recognize and manage potential complications promptly.
- Healthcare providers who perform procedures using the Seldinger technique should undergo specialized training and demonstrate proficiency in vascular access techniques, sterile procedures, and imaging interpretation. Training may be obtained through formal education programs, hands-on workshops, and clinical experience under supervision.
- Interested individuals can learn more about the Seldinger technique through medical textbooks, academic journals, online resources, and professional organizations specializing in interventional medicine and vascular access. Additionally, attending workshops or courses on vascular access procedures may provide valuable hands-on experience and training opportunities.



